|
Tutorial
HTML
Dreamweaver
|
s
Topic
10 - CGI Application Theory
CGI
-
Abbreviation
for "Common Gateway Interface".
-
This
is an interface standard which provides a method of executing
a server-side program (script) from a website to generate
a webpage with dynamic content.
-
Scripts
conforming to this standard may be written in any programming
language that produces an executable file, but are most often
written in Perl, Python, C, C++, or TCL.
-
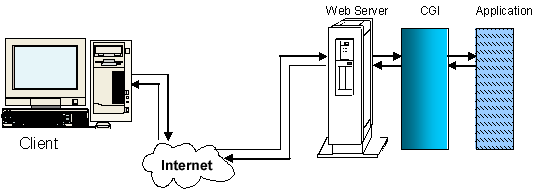
The
figure illustrates the interaction between client and server
when the client requests a document that references a CGI
script.
-
Often,
CGI scripts process information gathered from a form.
-
Permission
is granted within the web server (usually by the web master)
for specific programs on the server to be executed.
-
These
programs are typically designated with a certain filename
extension (such as .cgi or .pl) and/or located within a special
directory (such as cgi-bin).
-
After
the application output is sent to the server through CGI,
the results may be sent to the client.
-
Information
received by the client is usually an HTML or XHTML document,
but may contain images, streaming audio, Macromedia Flash
files, etc.
-
HTML
forms enable web pages to collect data from users and send
the data to a web server for processing by server-side programs
and scripts.
-
This
type of web communication allows user to interact with the
server and is vital to web development.
-
-
A
scripting language developed by Netscape to enable Web
authors to design interactive sites.
-
Although
it shares many of the features and structures of the full
Java language, it was developed independently.
-
JavaScript
can interact with HTML source code, enabling Web authors
to spice up their sites with dynamic content.
-
JavaScript
is endorsed by a number of software companies and is an
open language that anyone can use without purchasing a
license.
-
Recent
browsers from Netscape and Microsoft support it, though
Internet Explorer supports only a subset, which Microsoft
calls Jscript.
-
-
DHTML:
Abbreviation for dynamic Hypertext Markup Language.
-
A
form of HTML used to create Web page content that, as
perceived by the viewer, appears to change each time it
is viewed, without further interaction with the server.
-
The
Web-page content may use any of several technologies including
CGI scripts.
-
-
A
new language developed by Sun Microsystems.
-
It
allows executable programs called "applets"
to be distributed over the World Wide Web.
-
An
applet is written in Java and that part of the code, which
is system-independent, is compiled; the result is called
"bytecode".
-
When
a user clicks on a link that points to this bytecode,
the bytecode is downloaded onto the user's machine.
-
If
the user is using an appropriate Java-aware Web browser,
the browser contains an interpreter (specific to the user's
machine) which interprets the bytecode and allows the
user to run the applet.
-
-
Practical
Extraction and Report Language (PERL) is one of the most
widely used languages for web programming today.
-
Larry
Wall began developing this high-level programming language
in 1987 while working at Unisys.
-
Wall
wanted to create a language that would be more powerful
than shell scripting and more flexible than C, a language
with rich text-processing capabilities and most of all
a language that would make common programming tasks straightforward
and easy.
-
Most
of the information user send to servers is text, thus
Perl was a logical choice for programming the server side
of interactive web-based applications.
-
-
Active
Server Pages (ASP) a server-side technology that dynamically
builds documents in response to client requests.
-
The
ASP demonstrates communication between clients and servers
via the HTTP protocol of the World Wide Web.
-
When
a server receives a client's HTTP request, the server
loads the document (or page) requested by the client.
-
ASP
is a Microsoft technology for sending to the client dynamic
web content, including XHTML, Dynamic HTML, ActiveX controls,
client-side scripts and Java applets.
-
The
ASP processes the request (which often includes interacting
with a database) and returns the results to the client
- normally in the form of and HTML document, but other
data formats (e.g., images, binary data, etc.) can be
returned.
-
-
PHP
Hypertext Preprocessor, is quickly becoming one of the
most popular server-side scripting languages for creating
dynamic web pages.
-
PHP
was created in 1994 by Rasmus Lerdorf to track users at
his web site.
-
In
1995, Lerdorf released it as a package called "Personal
Home Page Tools."
-
PHP
2 featured built-in database support and form handling.
-
In
1997, PHP 3 was released, featuring a rewritten parser,
which substantially increased performance and led to an
explosion in PHP use.
-
The
release of PHP 4, which features the new Zend Engine and
is much faster and more powerful than its predecessor,
should further increase PHP's popularity.
-
PHP
is an open source technology that is supported by a large
community of users and developers.
-
PHP
is platform independent; implementations exist for all
major UNIX, Linux and Windows operating systems.
-
PHP
also provides support for a large number of databases,
including MySQL.
up
-
A
database is an integrated collection of data.
-
Many
companies maintain databases to organize employee information,
such as names, addresses and phone numbers.
-
A
database management system (DBMS) provides mechanisms for
storing and organizing data in a manner consistent with the
database's format.
-
Database
management systems allow users to access and store data without
addressing the internal representation of databases.
-
Relational
databases - composed of data that correspond to one another
- are the most popular database systems in use.
-
Almost
all relational database systems use a language called Structured
Query Language (SQL) to create queries and manipulate data.
-
Some
popular enterprise-level relational database systems include
Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, Sybase, DB2 and Informix.
 Client
/ Server Environment | Current Issues Client
/ Server Environment | Current Issues
Copyrights
Reserved © Web Publishing 2003
|
|
-
Assignment
1
-
Assignment
2
-
Quiz
1
-
Quiz
2
- Project
|
Announcement
To
all my students!
Please
visit this web site regularly.
|
|